
Catalytic glycolysis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) by solvent-free mechanochemically synthesized MFe2O4 (M= Co, Ni, Cu and Zn) spinel
Philip Anggo Krisbiantoro (Prof. Kevin C.-W. Wu’s group)
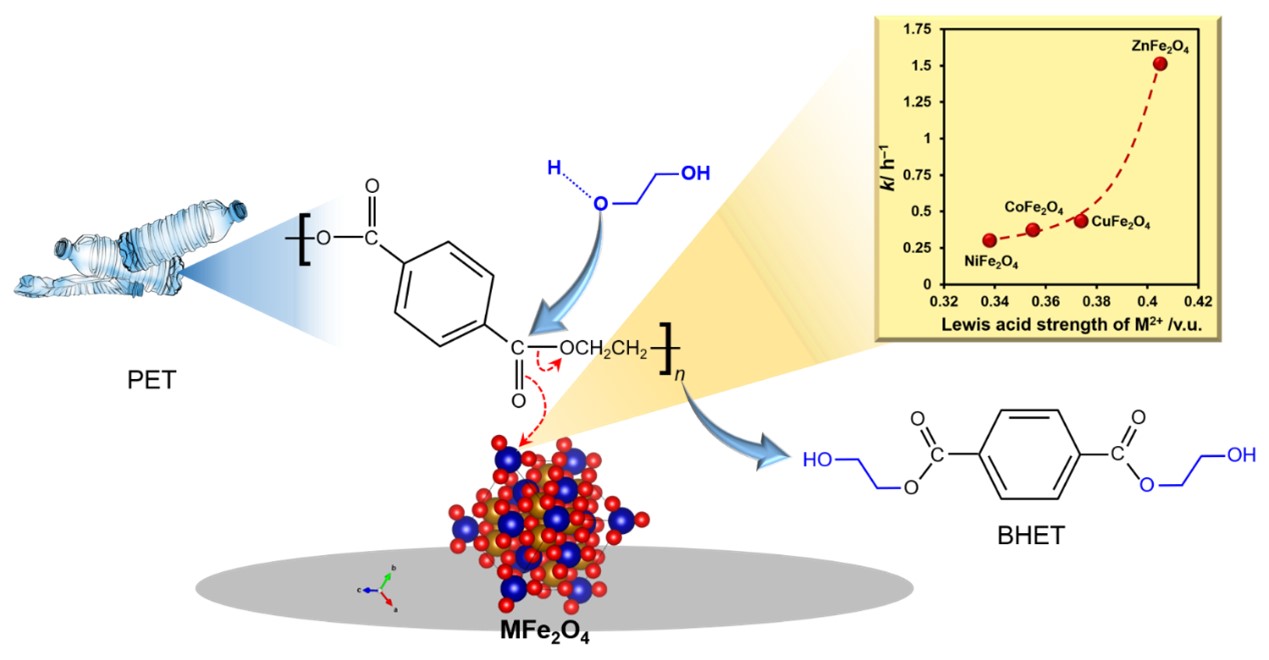
In the present study, the solvent-free mechanochemically synthesized MFe2O4 (M= Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn) spinel was used as a catalyst for PET glycolysis. All catalysts were active for PET glycolysis to produce bis(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (BHET) with the order of PET conversion of ZnFe2O4 > CuFe2O4 > CoFe2O4 > NiFe2O4. The catalytic activity was correlated with the Lewis acid strength of the M2+ in MFe2O4, i.e., a catalyst with strong Lewis acid exhibited high catalytic activity. Although CoFe2O4 was the second-best catalyst among the four in terms of yield of BHET, it possessed the highest saturation magnetization, which is a great advantage for magnetic separation of the catalyst. The reaction over CoFe2O4 exhibited apparent activation energy (Ea) of 188 kJ mol−1, and it was reusable for at least five times. Moreover, a simulation using Aspen Plus® software showed that scale-up is highly feasible.
This work has been published in Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450, 137926.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S138589472203412X



