The integration of materials with living matter opens new routes to improve our lives. Technological applications of biological processes can produce new structures and efficiently convert energy. On the other hand, the application of technology can enhance body functions and improve therapy. Finally, advances in characterization can shed light on important processes and cure diseases. MST researchers are working on many fundamental aspects of Bio-materials such as:
Biofabrication of Materials: The control over biological processes can be employed to produce new materials with unprecedented properties and structures.
Biointegration of Materials: When materials interact with biological systems, care has to be taken to provide suitable interfaces and biocompatible surfaces.
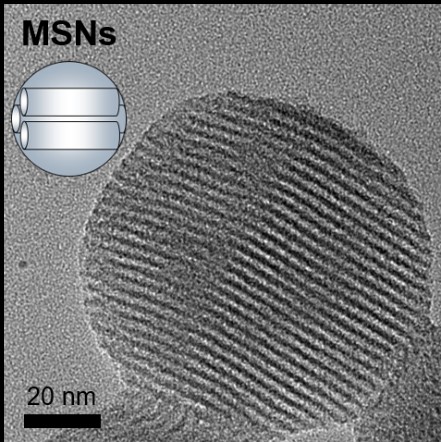
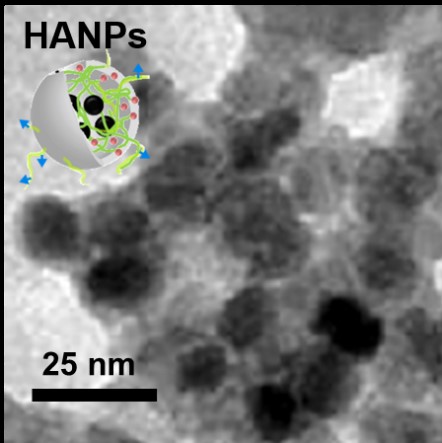
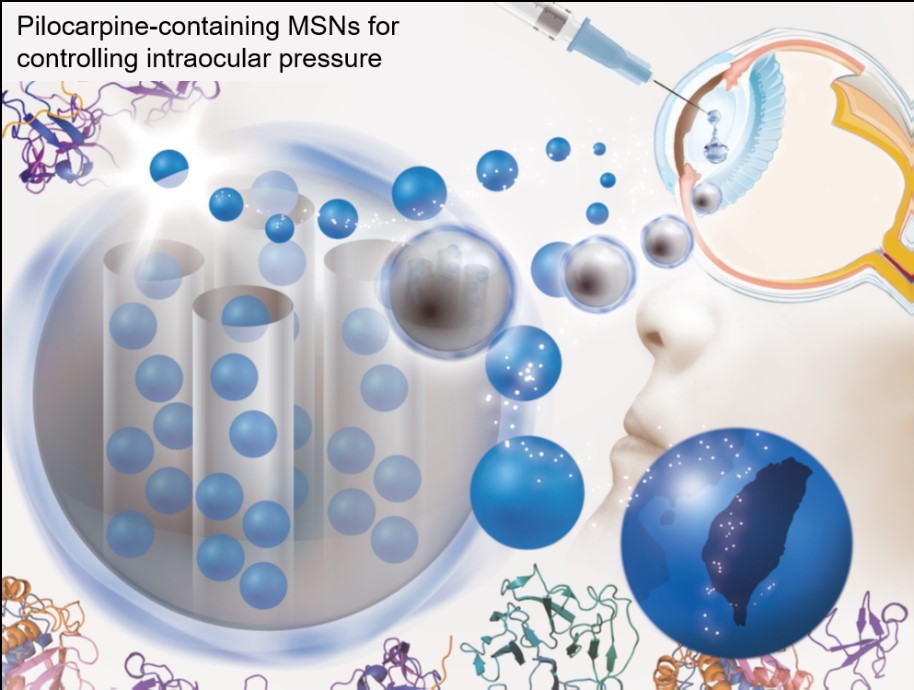
Nanoporous Materials: The surface of a material could be used to carry cargos, such as biomolecules, contrast agent. A porous material could carry more cargos compared with a non-porous material by its high surface area; furthermore, the surface properties of porous materials such as pore size, porosity, hydrophilicity could be modified for different applications. A drug delivery system (DDS) is developed by combination of nanoporous material and therapeutic molecules to promote the efficacy of drugs. A series of nanoporous material such as mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs), hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (HANPs) are synthesized by self-assembly and co-condensation with controllable physical and chemical properties. The nanoporous materials are characterized with transmission electron microscope and nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm to realize the morphology and surface area of carriers. Therapeutic drugs, pilocarpine is loaded into MSNs while doxorubicin is loaded into HANPs by a simple adsorption process. The release behavior of nanoporous was observed by monitoring the concentration of therapeutic drugs in a simulated environment. The pilocarpine-containing MSNs have a sustainable release behavior, showing a release of pilocarpine for 1 month, while doxorubicin-containing HANPs have a controllable release behavior, showing a release of doxorubicin only in acidic environment. The pilocarpine-containing MSNs are applied for controlling intraocular pressure (IOP) induced by glaucoma. The IOP of glaucomatous rabbit gets controlled for three weeks by injection of drug-containing MSNs. The doxorubicin-containing HANPs are applied for killing bladder cancer cells by intravesical therapy. The efficacy of doxorubicin on killing cancer cell is promoted around 20 times by loading doxorubicin into HANPs.